The Future of Military Operations: Hands-Free Technology on the Battlefield


The modern battlefield is undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, robotics, and sensor technologies. One of the most significant shifts is the move towards hands-free technology, a paradigm that promises to enhance soldier effectiveness, improve situational awareness, and ultimately, save lives. This article explores the burgeoning role of hands-free devices in military operations, examining their current capabilities and their potential to reshape the future of warfare.
The Limitations of Traditional Interfaces
Historically, soldiers have relied on handheld devices and manual controls for communication, navigation, and weapon systems operation. This traditional approach presents several limitations in the fast-paced, high-stress environment of combat:
- Divided Attention: Operating handheld devices requires soldiers to divert their attention from their surroundings, potentially compromising their situational awareness and increasing their vulnerability.
- Reduced Dexterity: Holding a device in one hand limits a soldier's ability to handle weapons, operate other equipment, or perform essential tasks like administering first aid.
- Increased Cognitive Load: Managing multiple devices and interfaces adds to a soldier's cognitive load, potentially leading to errors and slower reaction times.
- Compromised Physical Agility: The need to physically interact with devices can hinder movement, particularly in dynamic or confined spaces.
Hands-Free Technology: A Paradigm Shift
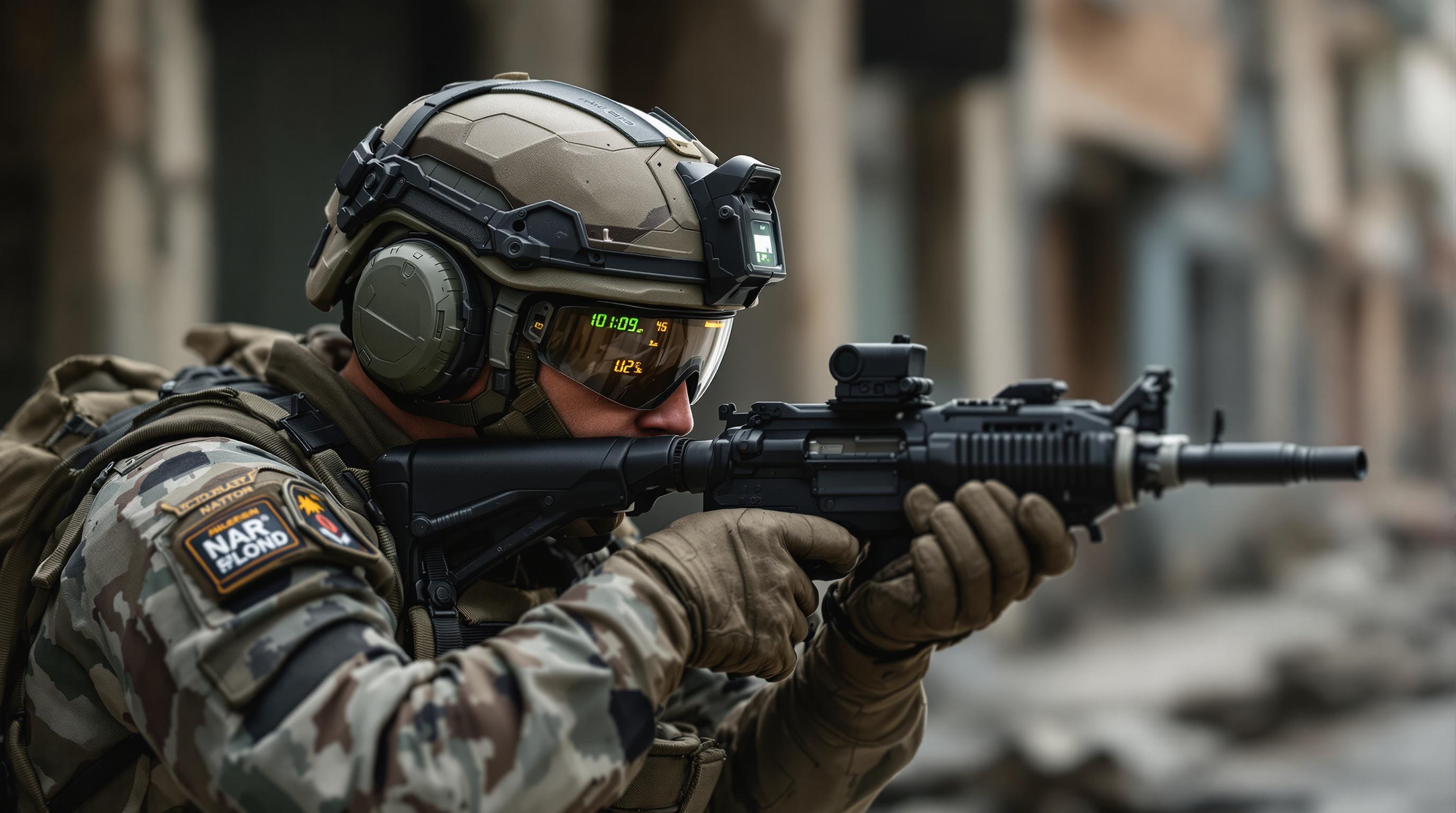
Hands-free technology offers a revolutionary alternative to traditional interfaces, freeing soldiers from the constraints of manual controls. By leveraging technologies such as voice control, gesture recognition, and augmented reality, hands-free systems enable warfighters to interact with their equipment and access critical information without ever having to take their hands off their weapons or their eyes off the mission.
Key Applications of Hands-Free Technology in Defense
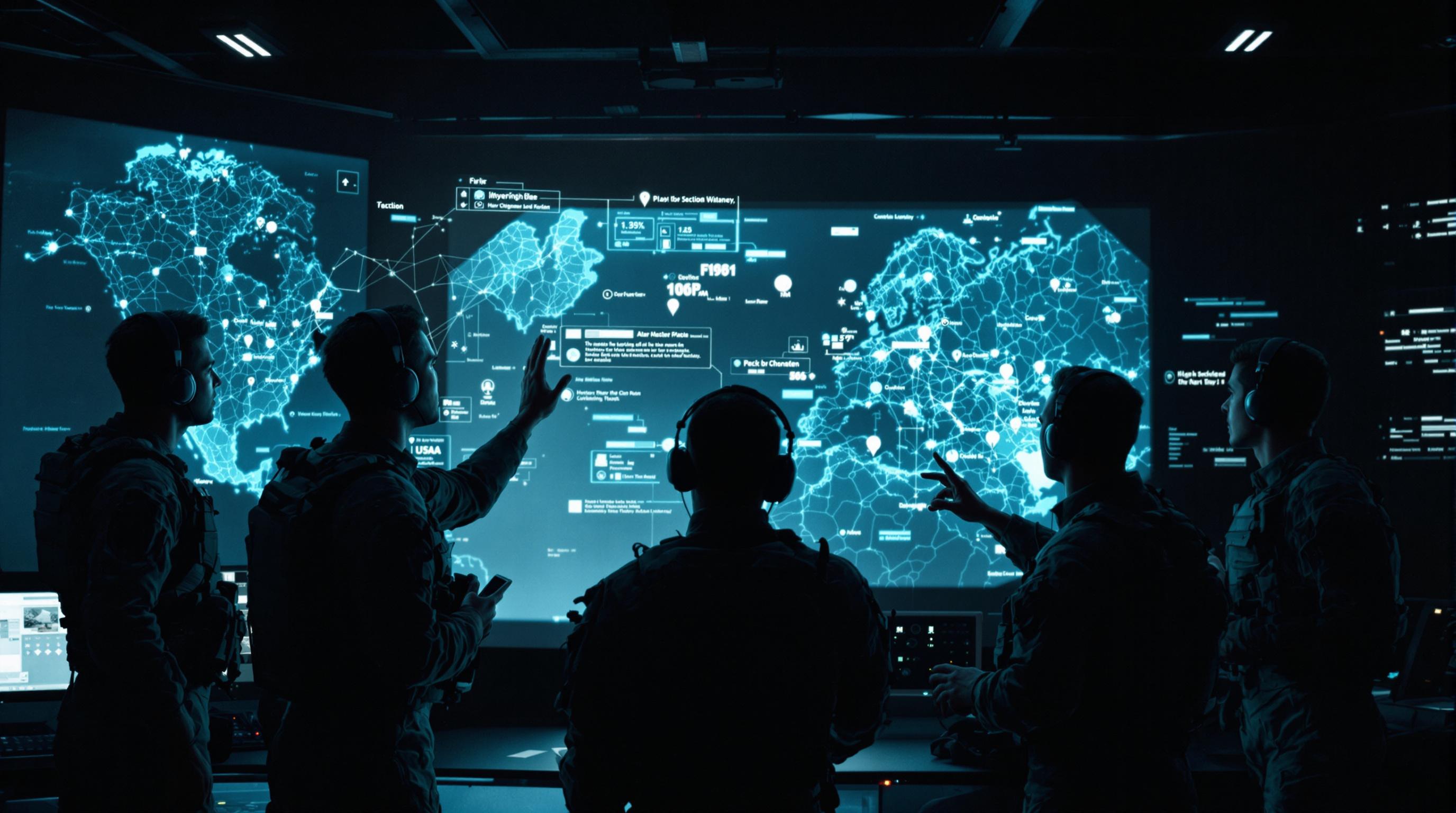
- Communication: Voice-controlled communication systems allow soldiers to stay in constant contact with their team members and command elements without the need for handheld radios. This enables seamless coordination and rapid information sharing, particularly during dynamic operations.
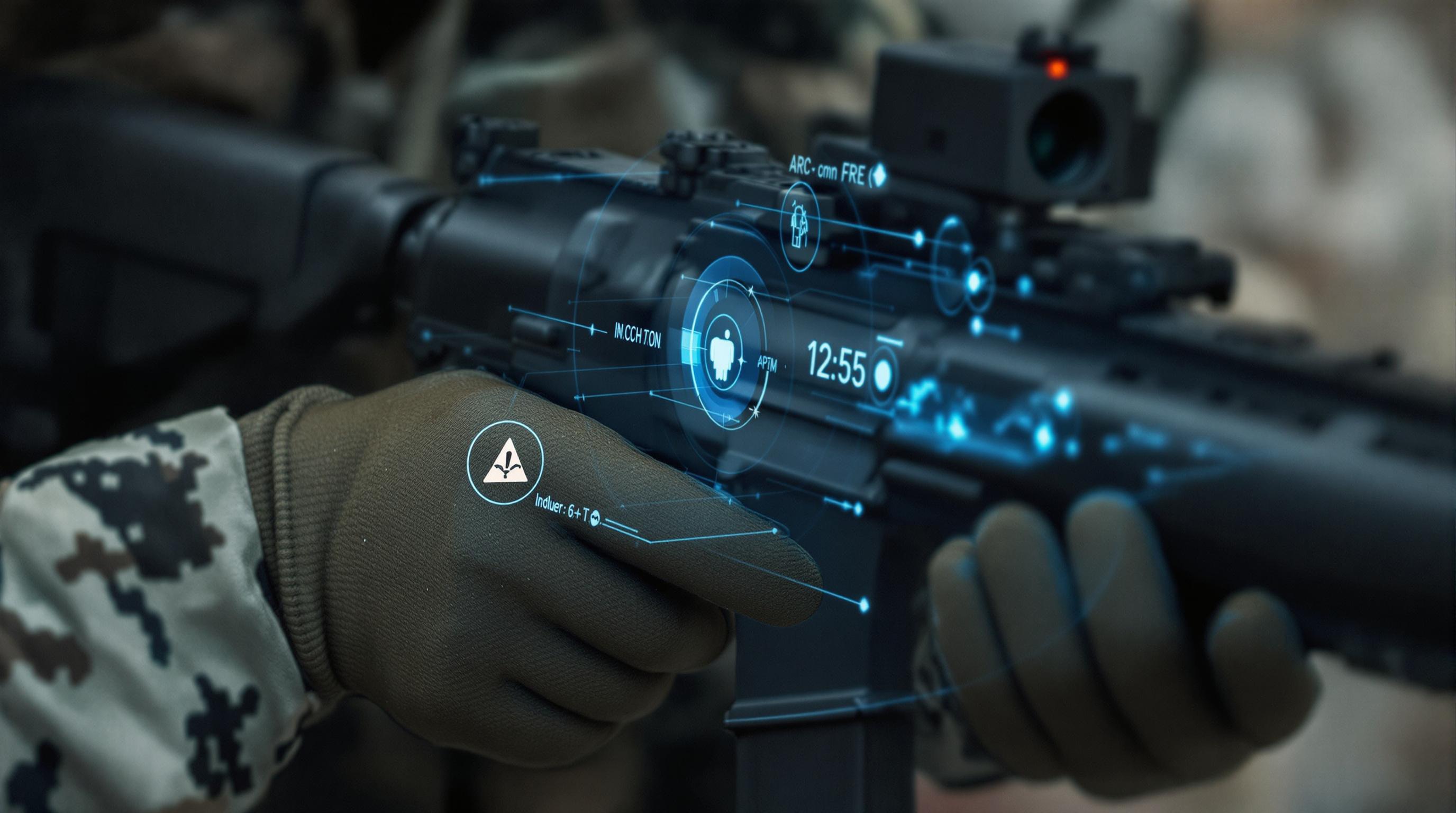
- Navigation: Augmented reality (AR) overlays, projected onto helmet visors or specialized eyewear, can provide soldiers with real-time navigation data, including waypoints, routes, and potential hazards. This eliminates the need to consult maps or handheld GPS devices, allowing them to maintain situational awareness while on the move.
- Weapon Systems Control: Future weapon systems may incorporate voice or gesture controls, enabling soldiers to select firing modes, adjust settings, or even designate targets without having to physically manipulate the weapon.
- Remote Platform Operation: Hands-free interfaces can be used to control unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs), and other robotic platforms. This allows soldiers to deploy and manage these assets while remaining fully engaged in their primary tasks.
- Medical Assistance: In the event of injury, hands-free devices can guide soldiers through self-aid procedures or facilitate remote medical assistance from medics or physicians located elsewhere.
The Future: Enhanced Situational Awareness and Cognitive Augmentation
The future of hands-free technology in military operations extends beyond simply replacing manual controls. It promises to enhance situational awareness and augment cognitive capabilities, creating a more intuitive and seamless interface between the soldier and their environment:
- AI-Powered Insights: Hands-free systems integrated with AI algorithms can analyze sensor data in real-time, providing soldiers with critical insights and alerts, such as threat detection, identification, and prioritization, without overwhelming them with raw data.
- Context-Aware Interfaces: Future systems will adapt to the soldier's context, automatically displaying the most relevant information based on the current situation, location, and mission objectives.
- Intuitive Interaction: Gesture recognition, eye tracking, and even brain-computer interfaces may eventually replace or complement voice control, creating even more natural and seamless interactions.
Conclusion
Hands-free technology is poised to revolutionize military operations, empowering soldiers with unprecedented levels of efficiency, situational awareness, and operational effectiveness. As the technology matures and becomes more integrated into military systems, it will fundamentally change the way soldiers interact with their equipment and the battlefield, paving the way for a more agile, adaptable, and lethal fighting force. The transition to a hands-free future is not just a technological advancement; it is a strategic imperative for maintaining a decisive advantage in the complex and rapidly evolving landscape of modern warfare.


